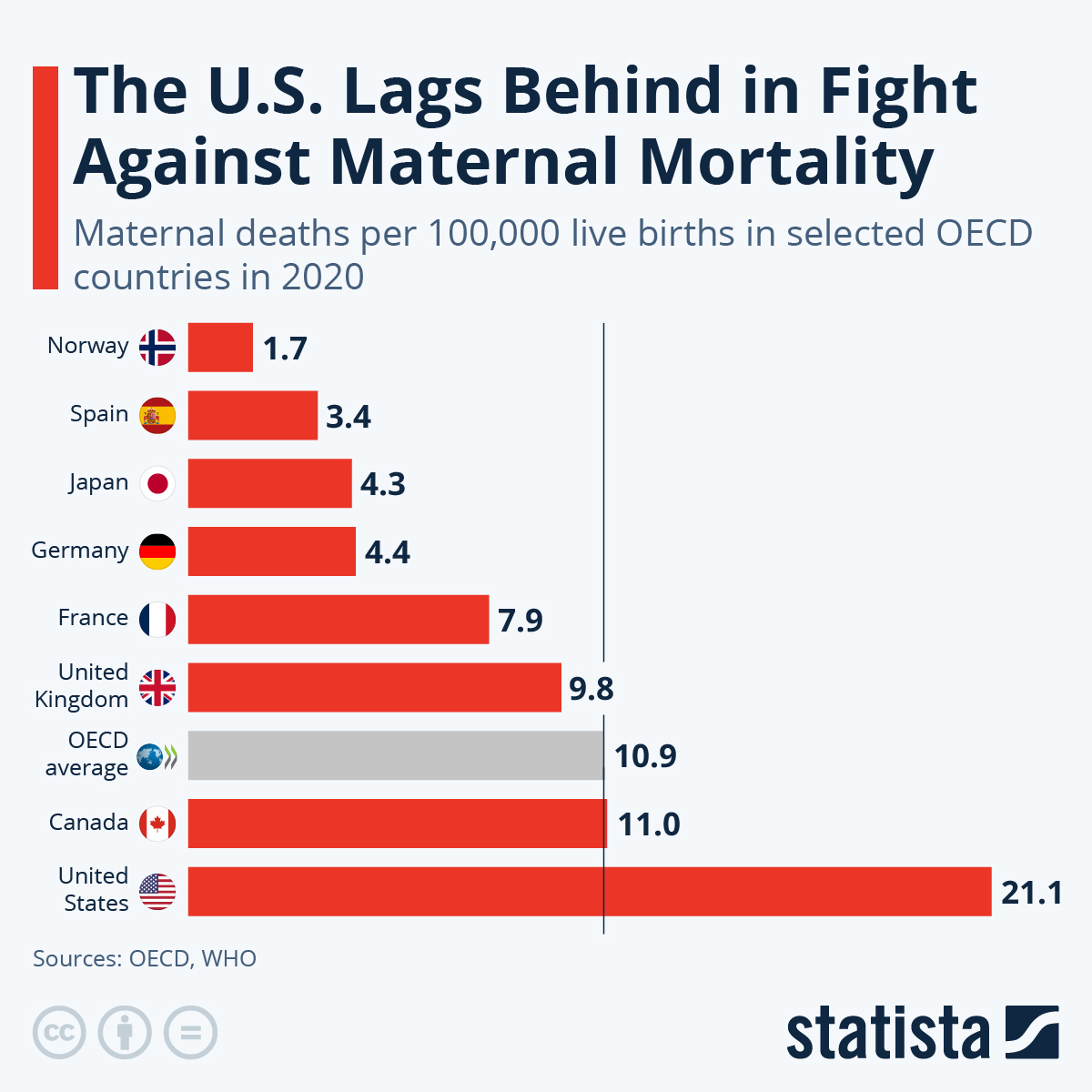
Maternal mortality remains a pressing public health issue, with alarming statistics indicating that the United States has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income nations. Recent studies reveal that the majority of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, yet the numbers continue to rise, highlighting a need for improved maternal health services. In 2022, there were 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births, a significant increase compared to 2018, exacerbated by disparities affecting racial and ethnic groups. To tackle this crisis, enhancing prenatal care and extending postpartum care will be crucial in reversing these trends. Addressing the high maternal mortality rate requires urgent attention and strategic public health investments to ensure safer pregnancies for all women.
The term “maternal mortality” refers to the tragic occurrences of deaths due to complications during pregnancy and childbirth. It is vital to understand that pregnancy-related deaths, which are often preventable, have been on the rise, particularly in high-income countries like the United States. This worrying trend underscores the necessity of improving women’s health throughout pregnancy and after delivery, with a focus on comprehensive maternity care and addressing systemic disparities. To effectively combat the high rates of maternal mortality, stakeholders must prioritize innovative solutions that enhance prenatal and postpartum care for mothers. Decreasing the incidence of pregnancy-related deaths will require collective efforts to reinforce maternal health systems and ensure equitable access to quality healthcare.
Understanding Maternal Mortality in the United States
Maternal mortality represents a critical health concern, particularly in the United States, which has seen a troubling rise in pregnancy-related deaths over the past several years. With more than 80 percent of these deaths being preventable, the experiences and challenges faced by pregnant individuals highlight the urgent need to address systemic deficiencies within our healthcare system. Studies indicate that the U.S. leads its high-income peers in maternal mortality rates, with significant disparities prevalent among different racial and ethnic groups. The statistics are alarming: American Indian women consistently face the highest mortality rates, underlining the need for inclusive and tailored maternal health interventions.
In addition to the disparities noted among various demographics, the rise in maternal mortality can also be attributed to broader societal issues, including lack of access to quality prenatal care, especially in maternity care deserts. Individuals in these regions often experience barriers that extend beyond healthcare systems, exacerbating risks during pregnancy. Cardiovascular health issues, which have now shifted to become the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, further illustrate the critical need for comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care that addresses chronic conditions as they relate to childbirth.
The Implications of Racial Disparities in Maternal Health
Racial disparities in maternal mortality continue to shock and alarm healthcare professionals and policymakers alike. Despite various efforts to reduce these inequities, the data remains stark; non-Hispanic Black women are disproportionately affected, with mortality rates significantly higher than those of white women. The systemic disparities entrenched in our healthcare system point to deeply rooted issues, including biased practices within medical communities and inequitable access to healthcare resources. These systemic injustices necessitate urgent reform to ensure that all pregnant individuals receive equitable and high-quality maternal healthcare.
Additionally, the focus on maternal health must encompass a wider range of factors that contribute to racial disparities, such as socioeconomic status, education, and access to necessary medical facilities. A comprehensive approach to improving maternal health outcomes should include targeted initiatives that work to bridge gaps in care, specifically aimed at the highest-risk populations. This involves not only improving quality of care during pregnancy but also addressing the social determinants of health that lead to heightened risks among diverse groups.
Improving Prenatal Care and Addressing Postpartum Needs
To effectively combat the rising rates of maternal mortality in the United States, investing in enhanced prenatal care is essential. A multifaceted approach could include expanding access to healthcare facilities that provide consistent and high-quality prenatal services, particularly for underserved populations. Strategic initiatives should aim to provide comprehensive education on pregnancy-related health issues, ensuring that expectant mothers understand the warning signs and have the support they need throughout their journey. Furthermore, extending the periods of care beyond the traditional six weeks postpartum can play a significant role in ensuring mothers receive the necessary support as they transition into parenthood.
Postpartum care is often neglected, despite a significant portion of maternal deaths occurring after childbirth. The importance of a continuous healthcare system for postpartum recovery has become increasingly evident, especially in light of high rates of late maternal deaths. Healthcare providers must prioritize maternal wellness well beyond delivery, offering resources and support that address potential complications, mental health challenges, and overall physical recovery. By integrating postpartum care into the continuum of maternal health, we can create a more supportive environment that fosters the health and safety of mothers and their infants.
The Role of Healthcare Policy in Maternal Health
The current state of maternal health in the United States reflects the urgent need for policy reform. With evidence indicating that various states experience vastly different maternal mortality rates, policymakers must pursue targeted strategies that improve the healthcare infrastructure at both local and national levels. Addressing systemic barriers, and advocating for equitable access to maternity care will be key to reducing pregnancy-related deaths across the board. Policymaking efforts must also consider social determinants of health, focusing on integrating strategies that empower individuals with the necessary resources to achieve better maternal health outcomes.
Furthermore, the collective responsibility of healthcare providers, state governments, and community organizations is pivotal in influencing policy changes. Engaging in open dialogues about the gaps in maternal healthcare, especially for marginalized communities, can lead to effective reforms that address disparities. Investing in policies that emphasize quality care and adequate funding for maternal health initiatives will ultimately benefit the entire population, fostering an environment where every individual has a safe and healthy pregnancy.
Rising Pregnancy-Related Deaths and COVID-19 Impact
The rise in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths has coincided with the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, which exacerbated existing challenges within the healthcare system. The initial months of the pandemic highlighted the vulnerabilities faced by pregnant individuals, many of whom experienced delayed access to essential prenatal services and increased risk of complications. As a result, many expectant mothers encountered heightened anxiety, leading to negative health outcomes that could be prevented with better access to care. Understanding these dynamics is critical in order to build resilient healthcare responses for future public health emergencies.
The pandemic’s influence goes beyond immediate healthcare access; it also underscores the importance of innovation in care delivery models. Exploring telehealth options and more flexible healthcare appointments could enhance prenatal care delivery, ensuring that pregnant individuals receive timely support despite external circumstances. As we analyze the implications of COVID-19 on maternal health, prioritizing research and investment in innovative prenatal care approaches must be central to our strategy in order to mitigate not only the immediate impacts but also long-term trends in pregnancy-related mortality.
Comprehensive Tracking of Maternal Deaths in the U.S.
One of the significant barriers to resolving maternal health issues in the United States is the lack of comprehensive tracking and understanding of maternal deaths. With the implementation of pregnancy checkboxes on death certificates beginning only in 2018, we have only started to capture a full picture of the problem. This delayed approach to data collection has hindered our ability to generate effective policies and interventions aimed at reducing maternal mortality rates. Improved tracking systems that accurately reflect the causes and circumstances surrounding maternal deaths are critical if we are to build a database that can inform future strategies.
Incorporating late maternal deaths into our analyses allows for a more nuanced understanding of maternal health dynamics over a full year post-pregnancy. As late maternal deaths are increasingly recognized as a vital part of the maternal mortality conversation, healthcare systems must adapt by incorporating protocols that address health issues affecting individuals well beyond traditional postpartum timeframes. This change sets the stage for targeted interventions that can effectively address the ongoing challenges faced by new mothers.
The Importance of Public Health Investment
Investing in public health infrastructure is pivotal for addressing the concerning trends observed in maternal mortality rates. Ensuring that our healthcare systems are equipped to handle the nuances of maternal health is not just a matter of moral and ethical duty, but also a public health necessity. Increased funding for maternal health programs can lead to better training for healthcare providers, wider availability of essential services, and a more robust public health response to pregnancy-related deaths. As the data illustrates, we are at a crucial juncture where proactive investment can lead to significant changes in maternal health outcomes.
Additionally, public health investments must also focus on fostering community-based initiatives that engage with local populations. By including community voices in maternal health strategies, policymakers can promote awareness and education that resonate at the grassroots level. Initiatives that prioritize support for vulnerable groups and emphasize culturally competent care are essential in creating a maternal healthcare framework that is both accessible and responsive to diverse needs. The evidence is compelling; as we move forward, sustained investment in maternal health must take center stage in our national health agenda.
Bridging Healthcare Gaps for Maternal Health
Bridging existing healthcare gaps is essential for improving maternal health outcomes across the United States. By focusing on enhancing access to quality care—especially for marginalized groups—we can work toward reducing the high rates of pregnancy-related mortality. This can involve various strategies, such as developing and implementing community health programs, improving transportation access to maternal health services, and ensuring that healthcare providers receive training in addressing specific needs of diverse populations. Collaborative efforts among stakeholders will be key in creating an integrated approach to maternal health.
Moreover, understanding the geographic disparities in maternal health is vital. States with lower pregnancy-related mortality rates offer valuable lessons for others to follow. Examining why certain regions excel in maternal care can provide insights into best practices and policy frameworks that can be adapted elsewhere. Creating a dialogue among states to share success stories and strategies fosters a collective effort to improve maternal health nationwide, helping to ensure that all individuals receive the quality care they deserve during the transformative experience of pregnancy and beyond.
Fostering Advocacy for Maternal Health Improvement
Advocacy plays a crucial role in elevating maternal health issues to the forefront of public discourse. Engaging advocates across various sectors—including health professionals, community leaders, and policymakers—can help amplify the urgency of addressing the rising maternal mortality rates in the U.S. By highlighting individual stories and statistical data, advocacy initiatives can shed light on disparities faced by specific groups and promote the need for immediate action. Awareness campaigns that educate the public on the factors contributing to pregnancy-related deaths can lay the groundwork for societal change.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of advocacy at the community level can empower individuals to demand better healthcare provisions for pregnant individuals. Mobilizing grassroots efforts can lead to demands for increased funding, better policies, and more comprehensive care pathways for maternal health. As more people become informed and engaged, they can become agents of change, influencing systemic reform in reproductive healthcare. By fostering a strong advocacy movement, we can work toward a future where the tragedies of maternal mortality are significantly reduced and where each pregnancy is met with the care and attention it rightfully deserves.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is maternal mortality and why is it a concern in the U.S.?
Maternal mortality refers to pregnancy-related deaths, specifically the deaths of women during pregnancy or within a year following the pregnancy. The U.S. has a high maternal mortality rate compared to other high-income countries, highlighting significant concerns about maternal health and the need for improved prenatal and postpartum care.
What are the main causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
The leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. include cardiovascular diseases, hemorrhage, and infection. Recent studies indicate that cardiovascular issues are responsible for over 20% of these deaths, emphasizing the urgent need for improved prenatal health monitoring and postpartum care.
How does the maternal mortality rate vary across different demographics in the U.S.?
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. show significant disparities by race and ethnicity. For example, American Indian and Alaska Native women have a markedly higher mortality rate compared to white women. These disparities underline the need for tailored maternal health policies to address the unique challenges faced by different groups.
What impact does the postpartum period have on maternal mortality?
The postpartum period, especially up to a year after childbirth, is crucial in assessing maternal mortality. Studies show that nearly one-third of pregnancy-related deaths occur after the first 42 days, indicating that extended postpartum care is essential for reducing overall maternal mortality rates.
What measures can be taken to improve maternal health and reduce mortality rates?
To improve maternal health and reduce mortality rates, investments must be made in comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care. This includes addressing systemic biases, expanding healthcare access in maternity care deserts, and implementing innovative solutions to enhance the quality of care for pregnant individuals.
How does maternal health policy influence pregnancy-related deaths?
Maternal health policies significantly influence pregnancy-related deaths by shaping healthcare access and quality. Differences in state-level policies can lead to varied maternal mortality rates, highlighting the need for cohesive strategies that ensure equitable healthcare across all populations.
How significant is the rise in maternal mortality rates between 2018 and 2022?
The rise in maternal mortality rates from 2018 to 2022 is alarming, with rates increasing from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births. This trend emphasizes the growing urgency for improved maternal health initiatives and effective healthcare infrastructure to combat rising pregnancy-related deaths.
What role does public health infrastructure play in addressing maternal mortality?
Public health infrastructure plays a crucial role in addressing maternal mortality by facilitating data collection, research, and implementation of health policies. Continuous investment in this infrastructure is essential to track maternal deaths accurately and develop strategies that enhance maternal health outcomes.
Why is it important to track late maternal deaths?
Tracking late maternal deaths, those occurring from 42 days to a year postpartum, is important because it reveals potential gaps in maternal care beyond the immediate postpartum period. Recognizing this can prompt healthcare systems to prioritize ongoing support and resources for new mothers.
What changes are needed to reduce the high maternal mortality rate in the U.S.?
Reducing the high maternal mortality rate in the U.S. necessitates systemic changes, including enhanced prenatal and postpartum care, addressing socioeconomic disparities, increasing medical research funding, and implementing effective health policies focused on reducing inequities in maternal health.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Preventability of Deaths | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. |
| Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, which rose from 25.3 deaths (2018) to 32.6 deaths (2022) per 100,000 live births. |
| Racial Disparities | Significant disparities exist, with American Indian/Alaska Native women having the highest mortality rate (106.3), followed by non-Hispanic Black women (76.9) and white women (27.6). |
| Major Causes of Death | Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death, accounting for over 20% of maternal deaths. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths (42 days to 1 year postpartum) account for nearly a third of total maternal deaths, highlighting the need for better postpartum care. |
| Health System Issues | The U.S. healthcare system struggles with inequitable policies, care deserts, and chronic medical conditions in younger populations. |
| Need for System Improvement | Investment in public health infrastructure and innovative solutions is essential to improve maternal health outcomes and address disparities. |
Summary
Maternal mortality continues to be a critical issue in the United States, where it ranks the highest among high-income countries. Addressing this urgent problem requires a multifaceted approach, including the improvement of prenatal and postpartum care systems. The alarming disparities based on race and state highlight the need for targeted policies and increased investment in healthcare infrastructure. Continued focus on the underlying causes, particularly chronic health conditions among pregnant individuals and access to equitable care, is essential to reduce preventable deaths and improve maternal health outcomes.