Alzheimer’s research is pivotal in our understanding and combat against this debilitating neurodegenerative disease, which afflicts millions worldwide. As scientists delve deeper, findings from researchers like Beth Stevens highlight the critical role of microglial cells in maintaining brain health by clearing away damaged cells and facilitating neural connections. However, when these cells malfunction, improper pruning may lead to conditions such as Alzheimer’s, thereby emphasizing the need for effective Alzheimer’s treatment and early detection. Recent advancements have also pointed towards the development of biomarkers for Alzheimer’s, which could revolutionize diagnosis and care. With the rising number of cases projected to double by 2050, the urgency of this research cannot be understated, as it holds the key to developing targeted therapies that could alleviate the burden on patients and their families alike.
Exploring the frontiers of Alzheimer’s disease investigation reveals a world where science strives to unravel the complexities of cognitive decline and memory loss. This field delves into various attributes of senile dementia, highlighting the importance of brain immunology and microglial function. Researchers like Beth Stevens are on a mission to discern the nuances of how immune responses within the brain contribute to neurodegeneration and affect the overall health of neuronal networks. By identifying potential biomarkers for Alzheimer’s, scientists aim not only to facilitate early diagnosis but also to pave the way for groundbreaking therapeutic interventions. As the push for innovative Alzheimer’s treatment intensifies, the world watches closely, hopeful for solutions that may change the landscape of care for affected individuals.
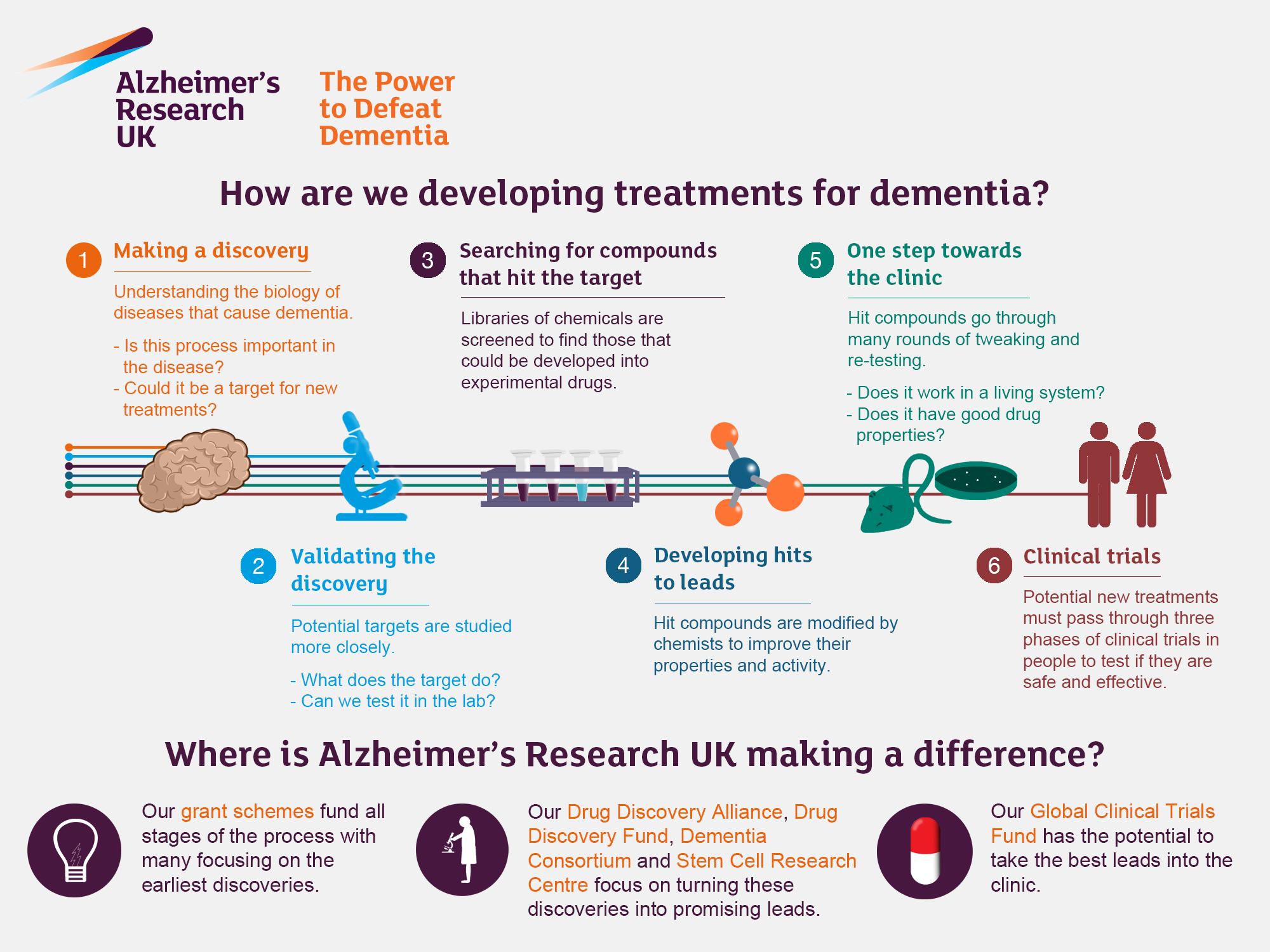
Understanding Microglial Cells in Alzheimer’s Research
Microglial cells are crucial to maintaining brain health, acting as the immune defense mechanism in the central nervous system. In the context of Alzheimer’s research, these cells are not merely passive bystanders but active participants in the pathophysiology of the disease. Recent studies have shown that improper functioning of microglia can lead to an increase in neuroinflammation, which is closely associated with the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. This revelation highlights the importance of targeting microglial activity to develop more effective treatment modalities.
As researchers like Beth Stevens delve deeper into the molecular mechanisms governing microglial behavior, they unveil potential therapeutic avenues that could mitigate Alzheimer’s effects. Understanding how these cells selectively prune synapses provides crucial insights into why cognitive functions decline in affected individuals. By identifying the signals that trigger these cells to become overly aggressive or dysfunctional, scientists hope to harness their potential for therapeutic strategies that slow or even reverse the neurodegenerative processes inherent in Alzheimer’s.
The Role of Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s in Early Diagnosis
Biomarkers play an essential role in Alzheimer’s research, offering a window into the disease process long before the manifestation of clinical symptoms. These biological indicators can include proteins found in cerebrospinal fluid or changes in brain imaging, which inform researchers and clinicians about the underlying neurodegenerative activity. Identifying reliable biomarkers is a critical step in developing early diagnostic tools that can distinguish Alzheimer’s from other neurodegenerative diseases, thus ensuring patients receive timely interventions.
The advancements made in the identification of new biomarkers are paving the way for innovative approaches to treatment. For instance, by coupling biomarker data with genetic and clinical information, researchers can stratify patients based on their risk profiles. This personalized medicine approach allows for more targeted and potentially effective interventions, addressing the unique characteristics and progression patterns of Alzheimer’s in individual patients. As emphasized by Stevens’ work, these early detection strategies are imperative for improving patient outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for those diagnosed.
Innovative Alzheimer’s Treatments Emerging from Research
The evolution of treatment strategies for Alzheimer’s has been significantly influenced by groundbreaking research like that conducted in the Stevens Lab. By shifting the narrative around microglial cells, scientists are now exploring how modulating the activity of these immune cells can lead to effective therapies. Current investigations aim to discover drug candidates that can either enhance the beneficial functions of microglia or inhibit their harmful actions, thereby providing a dual advantage in combating neurodegeneration.
Moreover, the nexus between basic science and clinical application cannot be overstated. Stevens’ research exemplifies how fundamental studies pave the way for translational breakthroughs. As new medications targeting specific pathways involved in neural pruning are identified, the potential for advancing Alzheimer’s treatment appears more promising than ever. These discoveries not only reflect the advancement of scientific knowledge but also embody hope for the millions affected by the disease.
The Importance of Basic Science in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Basic science serves as the foundational bedrock from which innovative therapies for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s emerge. While the immediate implications of experimental research may not seem apparent to everyone, the insights gained from studying fundamental biological processes are crucial. Steven’s work demonstrates that understanding the intricacies of microglial functions and their interactions within the nervous system is essential for unraveling the complexities of diseases such as Alzheimer’s—an endeavor that may initially appear distant from practical applications.
The exploration of neurodegenerative diseases requires a multidimensional approach, where basic scientific inquiry fuels the necessary understanding of underlying mechanisms. The knowledge generated through curiosity-driven research is what leads to breakthroughs that not only advance our understanding of diseases but also catalyze the development of effective treatments. As we continue to deepen our understanding of Alzheimer’s pathology, the integration of basic science into clinical research remains vital.
Funding and Support for Alzheimer’s Research Initiatives
Federal funding plays a crucial role in advancing Alzheimer’s research by providing resources for researchers like Beth Stevens. Grants from organizations such as the National Institutes of Health have historically supported studies aimed at unraveling the complexities of neurodegenerative diseases. This support is vital, especially in an era where the prevalence of Alzheimer’s is expected to rise dramatically, pushing the urgency for innovative research projects that can yield transformative treatments.
The significant impact of these federal grants illustrates the collaborative effort needed to tackle Alzheimer’s effectively. Sustained funding not only enables researchers to delve into uncharted scientific territories but also promotes a thriving ecosystem of innovation within academic institutions. This investment in basic and translational science is essential for catalyzing discoveries that may ultimately alter the trajectory of Alzheimer’s management and treatment.
Challenges in Alzheimer’s Disease Research
Alzheimer’s research faces numerous challenges, ranging from understanding complex disease mechanisms to translating findings into effective treatments. One major hurdle is the intricate nature of the biological processes involved, including neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration, which often interact in unpredictable ways. Research has shown that microglial cells, while beneficial in some contexts, can contribute to disease progression when their activity goes awry, complicating treatment strategies.
Moreover, the variability in how individuals experience Alzheimer’s symptoms adds another layer of complexity to research efforts. Factors such as genetics, environment, and co-existing health conditions can influence the course of the disease and responses to treatment. As a result, researchers are calling for more individualized approaches to Alzheimer’s research, combining insights from basic science with clinical data to develop targeted therapies and improvement strategies.
Current Perspectives on Alzheimer’s Treatment Advances
The ongoing advancements in Alzheimer’s treatment show that there is a concerted effort to improve therapeutic options. Recent developments in drug therapies are focusing on altering amyloid-beta and tau protein pathways, which are crucial in Alzheimer’s pathology. As ongoing research continues to seek effective ways to disrupt these neurotoxic processes, the potential for innovative pharmacological interventions becomes increasingly tangible.
In addition to pharmacotherapy, there is a growing interest in lifestyle interventions that could serve as adjunctive treatments. Emerging evidence suggests that physical exercise, cognitive training, and diet may have protective effects against cognitive decline. By integrating these approaches with the pharmacological advancements stems from Dorothy Stevens’ cutting-edge research on microglial cells and neuroinflammation, the future of Alzheimer’s management may rely on a multifaceted strategy that holistically addresses the disease.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Research: A Collaborative Approach
The future of Alzheimer’s research is increasingly leaning towards collaborative efforts that transcend traditional boundaries. By fostering partnerships among researchers, clinicians, and families affected by the disease, the scientific community can pool resources and knowledge to tackle Alzheimer’s collectively. This approach not only leads to a broader understanding of the disease but also enhances the applicability of research findings to real-world scenarios.
As seen in Beth Stevens’ groundbreaking work, collaboration can accelerate progress in understanding and treating Alzheimer’s. Engaging various stakeholders—from academic institutions to industry partners ensures that diverse perspectives are considered in research, ultimately driving innovation. This collaborative spirit is essential in the fight against Alzheimer’s, as it harnesses collective expertise to address one of the most pressing health challenges of our time.
The Societal Impact of Alzheimer’s Disease
The societal impact of Alzheimer’s disease extends beyond the individual, influencing families, care systems, and economies. With the number of Alzheimer’s cases projected to double by 2050, the burden on healthcare resources will significantly escalate. This shift underscores the need to prioritize research funding and establish robust healthcare frameworks to manage the increasing demands of care.
Additionally, the emotional and psychological toll on caregivers and families cannot be underestimated. The stress associated with caregiving often leads to mental and physical health issues for caregivers themselves. As society grapples with the challenges posed by Alzheimer’s, it becomes imperative to develop supportive programs that empower caregivers while also pushing for research that addresses the root causes and consequences of the disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role do microglial cells play in Alzheimer’s research?
Microglial cells are crucial in Alzheimer’s research because they function as the brain’s immune system. They monitor the brain for disease or injury, clearing away dead cells and pruning synapses. However, improper pruning by microglia has been linked to Alzheimer’s disease, highlighting their importance in understanding neurodegenerative diseases.
How are biomarkers for Alzheimer’s being identified through current research?
Current Alzheimer’s research focuses on discovering new biomarkers that can facilitate earlier detection of the disease. Studies, such as those conducted in the Stevens Lab, aim to uncover biological markers associated with the pathological changes in Alzheimer’s, which can lead to improved diagnostic tools and treatment strategies.
What advancements in Alzheimer’s treatment have emerged from recent neurodegenerative diseases research?
Recent advancements in Alzheimer’s treatment stem from research into neurodegenerative diseases, particularly the study of microglial cells and their role in synaptic pruning. These insights have paved the way for the development of medications that target the underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer’s, potentially altering its course and improving patient outcomes.
Who is Beth Stevens and what is her contribution to Alzheimer’s research?
Beth Stevens is a neuroscientist recognized for her groundbreaking research on microglial cells and their role in Alzheimer’s disease. Her work has shifted perceptions about these cells, demonstrating their involvement in neurodegenerative diseases and contributing to the identification of potential new treatments and biomarkers for Alzheimer’s.
Why is basic science important in the context of Alzheimer’s research?
Basic science is essential in Alzheimer’s research because it lays the foundation for future discoveries. It generates fundamental knowledge about brain function and diseases, which can advance understanding and lead to innovative treatments and therapies for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Focus | Beth Stevens focuses on the role of microglial cells in Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Importance of Microglia | Microglial cells function as the brain’s immune system, monitoring for disease and injury. |
| Connection to Alzheimer’s | Improper pruning by microglia is linked to Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative conditions. |
| Research Implications | Stevens’s research may lead to new medications and early disease detection biomarkers for Alzheimer’s. |
| Funding Sources | The research is primarily funded by the National Institutes of Health and other federal agencies. |
| Future Projections | The incidence of Alzheimer’s cases is expected to double by 2050, raising care costs significantly. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s research is advancing rapidly, particularly through the innovative work of scientists like Beth Stevens. As we delve deeper into the mechanisms of the brain’s immune system, particularly the role of microglial cells, we are uncovering vital insights that could pave the way for new treatments and early detection methods for Alzheimer’s disease. This research holds great promise for improving the lives of the millions affected by this debilitating condition.